How to Move From Outsourcing To Captive 2.0: The 2026 Transition Path
Global businesses are under pressure from rising costs, talent shortages, and constant demands for innovation. As a result, they are reimagining outsourcing as a Captive 2.0 model. This is a modern, tech-enabled global capability model that brings critical work back in-house.
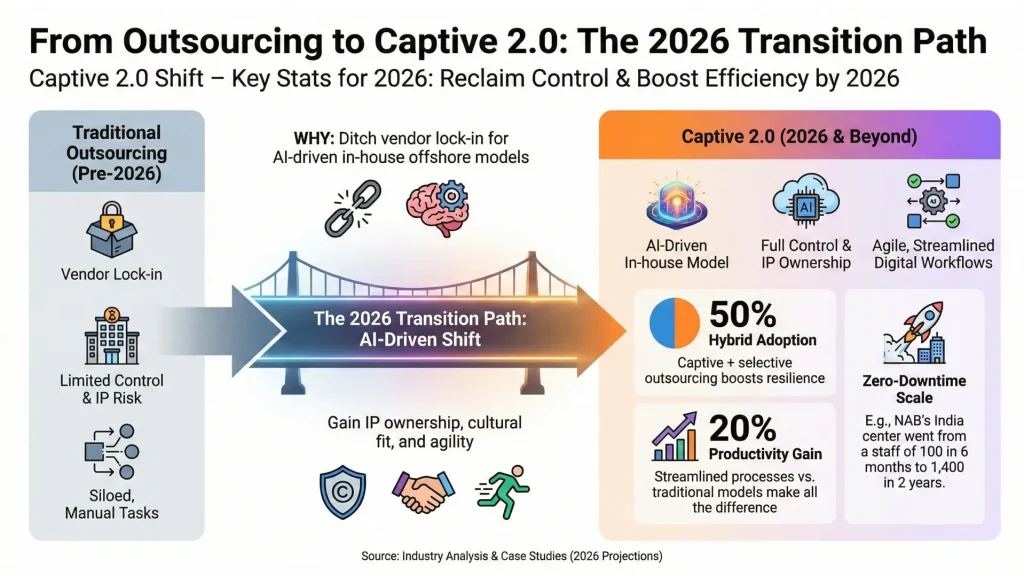
The shift strengthens intellectual property control and cultural alignment while speeding up decision-making. It also avoids the vendor lock-in risks of legacy outsourcing. Going into 2026, Captive 2.0 is becoming essential for agile and geopolitically resilient operations in an unpredictable world.
Data shows the shift is already underway. Industry reports indicate that most firms expect to move to a hybrid sourcing model, combining captive centers with selective outsourcing, by 2026. Captives also yield 30% productivity lifts in fulfillment teams versus conventional models, via streamlined processes and advanced skills.
The 2026 roadmap hinges on talent reskilling, tech modernization, and navigating compliance requirements, empowering pioneers to outpace rivals as outdated providers scramble.
Asset and Access Handover without Disruption
In the journey from outsourcing to Captive 2.0, a seamless asset and access handover is critical for business continuity. It minimizes downtime and protects institutional knowledge. It also reduces risks such as data loss and security breaches.
When companies prioritize structured documentation, collaborative knowledge transfer, and secure credential management, the transition happens without disruption. This ensures that captive teams inherit a strong foundation for innovation and scalability. Best practices emphasize phased planning, joint reviews, and post-handover validation to align outgoing and incoming teams.
Code, Data, Runbooks, Identity, and Secrets
Handover of core technical assets requires meticulous orchestration. Code, data, runbooks, identity, and trade secrets must transfer smoothly to empower the captive team. Live operations must remain uninterrupted throughout the transition.
This process starts with creating comprehensive inventories. It continues with interactive knowledge transfer sessions. Secure tools support every step of the transfer. All of this happens under strict compliance standards.
Here’s how companies can make this transition seamless and structured:
- Code Handover: Begin with a full audit of the codebase. List repository URLs, branch strategies, API endpoints, dependencies, and technical debt notes. Transfer access through version control systems like Git.
Support this with live demos and one-on-one sessions between developers to explain logic and best practices. This ensures the captive team can immediately deploy and iterate, reducing onboarding friction.
- Data Handover: Document database schemas, integration points, and residency requirements. Migrate data securely using backups and validation checks. Include recovery steps and performance metrics to maintain uninterrupted data flow. Run trial simulations to confirm integrity before the final cutover.
- Runbooks Handover: Compile playbooks for deployments, troubleshooting, CI/CD pipelines, and incident response. Share them through a centralized knowledge base. Add training workshops and Q&A sessions to embed these processes into the captive team’s daily routine. This prevents knowledge gaps.
- Identity and Secrets Handover: Set up role-based access controls for tools, servers, and cloud resources. Transfer sensitive information, such as API keys and passwords, using encrypted vaults like the HashiCorp Vault. Revoke old credentials after validation and enable multi-factor authentication (MFA). This minimizes unauthorized exposure and ensures compliance during the transition to internal ownership.
Talent and Knowledge Transfer Playbooks
In the shift to Captive 2.0, talent and knowledge transfer playbooks become the blueprint. They keep continuity intact. They prevent operational disruption an unlock the true strategic value of in-house centers.
These playbooks define how expertise moves from vendors to internal teams. They capture explicit knowledge like documented processes. They also capture tacit knowledge like unwritten insights and skills.
A well-executed playbook speeds up the transition and drives innovation. It embeds global talent pools directly into the organization’s core operations. Key components include phased planning, clear role assignments, defined timelines, and digital repositories for knowledge capture.
The process also fosters a culture of knowledge sharing to support long-term agility across Global Capability Centers. When companies prioritize these elements, they can finally move from vendor dependency to building owned innovation hubs. This reduces talent and continuity risks and ensures smooth integration.
Shadow/Reverse Shadow and Acceptance Criteria
Shadowing and reverse shadowing are cornerstone techniques in knowledge transfer playbooks. They work especially well for capturing tacit knowledge during outsourcing to captive transitions.
Shadowing puts the incoming captive team in observation mode. They watch the outgoing vendor’s operations in real time through workshops, maintenance tasks, debugging sessions, and daily workflows. This helps them absorb undocumented practices and build contextual understanding. The process usually runs for two to three weeks. It allows the new team to experience real responsibilities firsthand and develop trust, cultural alignment, and confidence in handling complex decisions.
Reverse shadowing flips the structure. The vendor team watches the captive team perform tasks. They verify knowledge absorption, identify gaps, and give immediate feedback. It follows once roughly 90 percent of the handover is complete. This step simulates real scenarios and resolves issues before full independence, ensuring a smooth shift to steady state.
Together, shadowing and reverse shadowing—often supported by mentorship—keep disruption low in high-stakes environments like IT support or GCC setups. They speed up time-to-market and enable faster delivery of co-created solutions.
To validate success, organizations must define clear acceptance criteria upfront in the playbook. These should include measurable milestones such as:
- Knowledge Completion Threshold: The shadow phase should only begin once all core processes have been documented in detail and validated to ensure readiness for hands-on transition work.
- Defect and Issue Metrics: Post-transfer defect rates aligned with severity classifications (e.g., critical issues resolved within SLAs), ensuring the captive team handles 95% of incidents independently.
- Feedback and Validation Loops: Stakeholders sign off on reverse shadowing sessions, confirming no major gaps via surveys or audits, alongside timelines for full handover (e.g., 4-6 weeks total).
- Performance Baselines: Alignment with business KPIs, such as reduced resolution times by 20% post-transition, to quantify ROI.
Conclusion
The shift from outsourcing to Captive 2.0 represents a structural upgrade in enterprise capability. It strengthens resilience, control, and long-term value creation. By investing in clean handovers and structured knowledge transfer, companies reduce external dependence.
Talent-led operating models then drive faster innovation and stronger business continuity. Organizations that take this approach are best poised to enter 2026 with sharper governance, clearer IP ownership, and a scalable foundation built to withstand geopolitical and technological volatility.
Consider this use case. In 2022, a leading financial institution partnered with ANSR to launch an India-based Innovation Center, addressing common outsourcing challenges by sourcing top talent in cloud, cybersecurity, data engineering, AI/ML, and technical architecture. ANSR enabled a smooth GCC transition, onboarding a 100-member core team in six months through phased shadowing and secure migration of code, data, and access controls.
This resulted in full in-house ownership, zero disruption, and rapid growth to 1,400 staff in under two years. Productivity increased through AI-driven automation and upskilling. The organization regained IP control, eliminated vendor lock-in, accelerated innovation, and strengthened geopolitical resilience, demonstrating Captive 2.0’s high ROI in finance.
Want to know how your enterprise can ramp up gains with a GCC? Partner with ANSR for seamless transitions, from asset handovers to talent reskilling. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and fast-track your 2026 roadmap.




