Industry-specific GCC Considerations: BFSI, Retail, and Manufacturing
Industry-specific GCC considerations vary widely across BFSI, retail, and manufacturing, shaped by each sector’s unique priorities and constraints. GCCs are no longer built on one-size-fits-all models; they reflect different risk profiles, transformation goals, and scale needs. These differences directly influence how organizations invest in capabilities, structure teams, and integrate GCCs into the wider enterprise.
BFSI GCC strategy focuses on compliance, security, and operational resilience within highly regulated environments. Retail GCCs move at speed to deliver personalized, data-led experiences across markets. Manufacturing GCCs emphasize engineering depth and innovation to support smart factories and modern production.
Recognizing these differences is essential to building GCC strategies that truly fit the industry.
Why GCC Strategies Differ by Industry
GCC strategies vary by industry due to differences in risk, regulation, and value drivers. BFSI GCC strategy focuses on compliance and resilience, and retail on analytics and customer experience. The manufacturing GCC model focuses on engineering, R&D, and smart factory enablement.
Regulatory, Customer, and Supply-chain Realities
Industry-specific GCC considerations and strategies differ as customers want speed, experience, and service outcomes. To match evolving consumer behaviors, retail GCCs prioritize:
- Personalization
- Omnichannels
- Rapid experimentation
These centres invest heavily in:
- Analytics
- AI-driven recommendations
- Responsive digital platforms
Success depends on:
- Agility
- Continuous optimization
- Close alignment with customer journeys
Supply-chain realities further shape how GCCs are designed and scaled across industries. The manufacturing GCC model operates within asset-intensive, globally distributed supply networks requiring precision and resilience. To improve production continuity and inventory management, these teams support:
- Demand forecasting
- Supplier coordination
- Control towers
- Operational analytics
In BFSI, supply chains are information-driven and tightly regulated, pushing GCCs to focus on governance, data quality, cybersecurity, and compliance. This enables secure digital operations, effective risk management, and trusted service delivery.
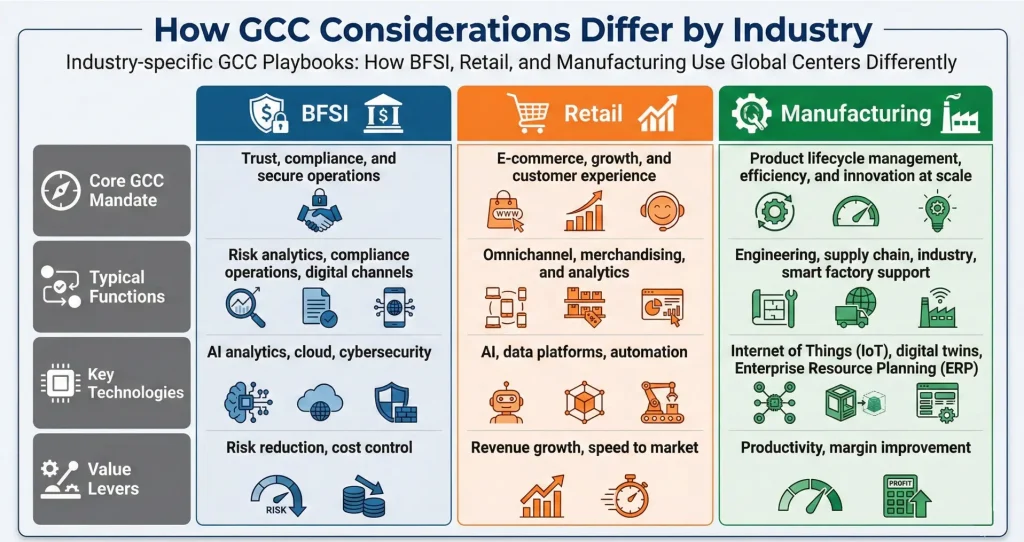
Variations in Digital and Data Intensity
Industry-specific GCC considerations because digital and data intensity vary significantly across business models. BFSI operates in data-heavy, highly regulated environments that demand precision and real-time insight. This pushes GCCs to prioritize:
- Advanced analytics
- Cybersecurity
- Fraud detection
- Strong data governance
Retail and manufacturing exhibit different digital and data intensity patterns shaping GCC priorities. The retail GCC model relies on high-volume, fast-moving customer data enabling:
- Personalization
- Demand forecasting
- Omnichannels
Manufacturing focuses on operational data, engineering systems, IoT signals, and predictive maintenance analytics. These variations need GCCs to tailor platforms, talent, and operating models. Below are the GCC use cases by industry in brief.
BFSI GCC Considerations
BFSI GCC strategy is designed to manage high-risk, regulation-heavy, and security-critical environments. Industry-specific GCC considerations reflect the need for resilience, trust, and continuous regulatory alignment.
Risk Management Hubs
- Enable real-time credit, market, and operational risk monitoring using advanced analytics.
- Deploy predictive models to shift from reactive to proactive risk management.
- Centralise enterprise risk data across geographies and business lines.
- Use AI-driven surveillance to detect fraud, anomalies, and behavioural risks early.
- Support CROs with scenario modelling and stress-testing capabilities.
Compliance and Regulatory Hubs
- Operationalise global regulations, including requirements of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), and other regulatory bodies.
- This includes Know Your Customer (KYC), sanctions screening, and regulatory reporting.
- Maintain audit readiness through digital documentation and compliance dashboards.
- Manage multi-jurisdictional compliance through domain-led legal and regulatory expertise.
- Reduce non-compliance risks while improving institutional credibility and transparency.
Secure Operations and Cybersecurity Hubs
- Run 24X7 security operations centres for threat detection and incident response.
- Implement cyber threat intelligence to identify attack vectors in real time.
- Enforce ISO, PCI-DSS, and SOC-certified security frameworks across systems.
- Strengthen data privacy, identity access management, and cloud security controls.
- Integrate fintech, academia, and startups to future-proof cybersecurity capabilities.
Data Platforms
- Robust data platforms are critical for ensuring compliance with global financial regulations. Some of these include:
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDP)
- Basel III
- PCI-DSS mandates
- Unified data architectures can cut silos across retail, corporate, and treasury functions.
- Strong data governance ensures standardized definitions, metadata management, and single sources of truth.
- End-to-end data lineage enables audit transparency, faster issue resolution, and regulator-ready reporting.
- Built-in quality controls prevent reporting errors that could impact risk and compliance outcomes.
- Cloud-native, scalable platforms help modernize legacy core banking and finance systems securely.
- Encryption, role-based access, and zero-trust security are essential for sensitive financial data.
- Platforms must handle high transaction volumes while supporting real-time risk and fraud analytics.
- Integrate with Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Machine Learning Operations (MLOps) to enable advanced use cases such as fraud detection and KYC automation.
- Modular architectures allow faster regulatory updates without disrupting existing operations and digital channels.
Fraud Analysis
- Design real-time fraud analytics platforms aligned with Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Financial Action Task Force (FATF), Anti-Money Laundering (AML), and Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDP) mandates.
- Prioritise adaptive models to handle evolving fraud patterns and behavioural shifts.
- Embed adversarial testing to strengthen resilience against data poisoning and model manipulation.
- Implement continuous drift detection to maintain accuracy in high-velocity transaction environments.
- Ensure strong data quality controls across ingestion, preprocessing, and feature engineering pipelines.
- Integrate human-in-the-loop reviews for model validation, escalation, and regulatory confidence.
- Build explainable fraud models to support auditability and regulator scrutiny.
- Maintain end-to-end data lineage to trace fraud decisions across systems and workflows.
- Adopt cloud-hybrid architectures with MLOps for scalable, compliant fraud operations.
- Enable secure cross-border data integration without violating localization requirements.
- Align fraud KPIs with business outcomes like reduced false positives and faster resolution.
- Invest in domain-skilled talent combining fraud, risk, and advanced analytics expertise.
Digital Channels
- Prioritise cloud-native digital channels to support high transaction volumes and real-time services.
- Embed AI-driven personalization across mobile, web, and API-led customer journeys.
- Ensure regulatory alignment across regions through unified compliance-aware digital platforms.
- Design omnichannel architectures enabling seamless handoffs between assisted and self-service channels.
- Modernise legacy systems using microservices and strangler patterns for faster digital releases.
- Build zero-trust security into digital channels to protect identities, payments, and data flows.
- Enable scalability and resilience to handle peak loads, fraud spikes, and market volatility.
Retail GCC: Factors to Consider
Retail GCCs focus on speed, customer insight, and execution excellence to support dynamic and experience-led business models.
Omnichannel
- Integrate physical stores, e-commerce, mobile apps, and social channels into one experience.
- Enable seamless transitions across channels without losing customer context or transaction history.
- Support click-and-collect, endless aisles, in-store digital touchpoints, and unified loyalty programs.
- Centralise customer data to power consistent personalization across online and offline journeys.
- Ensure real-time inventory visibility and fulfilment coordination across all customer-facing and operational retail touchpoints.
E-commerce
- Build scalable commerce platforms supporting high traffic, peak loads, and rapid feature releases.
- Enable AI-driven inventory, demand forecasting, and pricing to improve fulfilment accuracy.
- Strengthen last-mile logistics integration across warehouses, partners, and delivery ecosystems.
- Modernise ERP and order management systems for real-time visibility and orchestration.
- Support vertical marketplaces and niche commerce models with flexible, modular architectures.
Customer Analytics
- Build unified Customer 360 views across POS, digital, loyalty, and in-store interactions.
- Apply behavioural analytics to understand journeys, preferences, and purchase drivers across channels.
- Use AI and ML models to predict churn, purchase intent, and promotion responsiveness.
- Enable real-time personalization across websites, apps, emails, and in-store touchpoints.
- Support customer segmentation and Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) modelling to prioritise high-value customers and optimise spending.
Merchandising
- Enable data-led assortment planning using demand forecasts and localized customer preferences.
- Support dynamic pricing and promotion optimization through AI-driven elasticity models.
- Power inventory-to-sales alignment by integrating merchandising with supply chain analytics.
- Leverage AI agents to automate product classification, catalogue enrichment, and lifecycle management.
- Deliver real-time performance insights across categories, regions, and channels.
Pricing
- Enable data-driven pricing models using demand signals, costs, and competitive intelligence.
- Support private-label pricing strategies to balance quality perception and cost leadership.
- Build dynamic pricing engines for promotions, markdowns, and localized market conditions.
- Optimise price architecture across channels to ensure consistency and margin protection.
- Scale pricing analytics rapidly across regions using standardized platforms and automation.
Marketing Operations
- Centralise campaign planning, execution, and reporting across regions and digital channels.
- Enable marketing automation, analytics, and MarTech platforms for faster go-to-market cycles.
- Support data-driven personalization using customer insights, segmentation, and performance metrics.
- Ensure brand governance, compliance, and quality assurance across global marketing assets.
- Foster collaboration between global teams, agencies, and local market stakeholders.
Manufacturing GCC Considerations
Manufacturing GCCs are designed to support engineering depth, operational precision, and long-term innovation.
Engineering
- Build scalable, cloud-native architectures supporting complex product engineering systems, plant operations, and industrial workloads.
- Modernize legacy manufacturing systems such as Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP). Use microservices (MS) and Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to improve system flexibility and integration.
- Enable AI and automation engineering for production planning, quality optimization, predictive maintenance, and operational forecasting.
- Support DevOps, CI/CD pipelines, and platform reliability for rapid feature releases.
- Integrate engineering, operations, and supply-chain systems to ensure end-to-end manufacturing platform stability.
PLM (Product Lifecycle Management)
- Build digital PLM systems enabling real-time collaboration across design, sourcing, and manufacturing teams.
- Use digital twins to accelerate design validation, simulations, and faster product iterations.
- Embed cost, compliance, and sustainability checks directly into engineering workflows.
- Integrate AI and analytics to optimize materials, lifecycle costs, and product quality.
- Support closed-loop feedback using data from stores, suppliers, and connected products.
Industry 4.0 Capabilities
- Enable digital twins for real-time product, supply chain, and lifecycle simulations.
- Integrate IoT sensors to track inventory movement, asset performance, and store operations.
- Apply AI and analytics for predictive demand forecasting, production optimization, and capacity planning.
- Embed automation and robotics insights to optimize fulfilment, warehousing, and last-mile efficiency.
- Support closed-loop decision-making by linking design, operations, and sustainability data.
Supply-chain Visibility
- Enable real-time visibility across inventory, suppliers, warehouses, and last-mile delivery networks.
- Integrate Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), Transportation Management Systems (TMS), and external signals into unified supply-chain data models.
- Build digital control towers for centralized monitoring and coordinated exception management.
- Use AI and analytics to predict disruptions and recommend corrective actions proactively.
- Improve decision speed through live dashboards, alerts, and scenario-based simulations.
Smart Factory Support
- Enable real-time production monitoring using IoT sensors and advanced analytics platforms.
- Support digital twins to simulate production scenarios and optimize throughput and quality.
- Integrate energy analytics to reduce waste and meet sustainability and ESG commitments.
- Provide predictive maintenance insights to minimize downtime across manufacturing GCC model partners.
- Standardise data integration between factories, suppliers, and retail planning systems.
Choosing the Right GCC Design for Your Industry
Selecting the right GCC design requires clarity on purpose, talent needs, and geographic strategy. Industry context determines how GCCs scale value, manage risk, and deliver long-term impact.
- Mandate Definition: Clearly define whether the GCC supports core operations, innovation, or end-to-end ownership.
Regulated industries require compliance-led mandates, while digital sectors prioritize speed and experimentation.
- Talent Profile: Talent requirements vary by industry, digital intensity, domain complexity, and risk exposure.
BFSI GCC strategy demands compliance, risk, and cybersecurity expertise, while retail prioritizes analytics and skills.
- Location Filters: Location choices depend on talent depth, ecosystem maturity, and long-term scalability needs.
Tier-1 cities suit complex innovation roles, while Tier-2 hubs support cost-efficient, scalable operations.
Industry-specific GCC considerations succeed when aligned with regulatory intensity, customer expectations, and operational complexity. ANSR helps enterprises design, build, and scale industry-aligned GCCs with speed and confidence. Our services span location, operating model design, talent buildout, governance, and digital transformation according to industry-specific GCC considerations. Partner with ANSR to transform your GCC into a strategic growth engine.




