Are Your Centers GCC-Ready? A Practical Health and Performance Review
With India now home to 1,800+ Global Capability Centers (GCCs) employing over 2.1 million professionals, GCC transitions have become a central part of global operating models. A GCC readiness assessment usually starts with a straightforward review of how current centers function. This helps organizations understand their operational maturity, governance practices, and compliance levels.
It also evaluates whether the center’s setup aligns with long-term goals across offshore or nearshore models. By looking closely at delivery consistency, process discipline, and risk management, leaders get a clearer sense of how stable and dependable the operation really is.
A comprehensive GCC audit framework reviews performance metrics, talent quality, retention trends, and leadership depth. Additionally, it assesses process efficiency, data security, regulatory adherence, and the effectiveness of controls. This assessment reveals whether the organization can move toward strategic control, scalability, and value creation.
Why GCC Readiness Starts with an Honest Audit
GCC readiness begins with understanding current operational realities, not future aspirations. An honest audit exposes structural gaps, hidden risks, and scalability limits early. Without this clarity, organizations risk scaling inefficiencies instead of building strategic capability centers.
Limitations of Current Offshore and Nearshore Setups
An objective audit evaluates how offshore and nearshore setups perform beyond cost efficiency. It examines governance maturity, talent sustainability, innovation readiness, and risk exposure holistically.
This GCC readiness assessment helps leaders identify whether current models support long-term value creation. It also clarifies which limitations could hinder a successful transition to a GCC. These include factors such as:
- Time zone differences, slow decisions and real-time collaboration
- Language nuances can cause misunderstandings and errors
- Cultural gaps may weaken trust, cohesion, and engagement
- Maintaining quality is hard without strong governance
- Data security risks increase across multiple legal frameworks
- Geopolitical instability can disrupt operations and contracts
- Limited onsite presence reduces operational visibility
- Frequent leadership visits raise travel costs
- Nearshore labor costs reduce cost advantages
- Specialized skills may be scarce, raising salaries
- Economic volatility affects workforce availability and costs
- Regulatory differences increase compliance complexity
Triggers That Demand a More Strategic Model
GCC readiness often emerges when existing operating models depict structural strain. An honest GCC audit framework helps leaders recognize when incremental fixes no longer work. These triggers signal the need to shift from tactical delivery to a strategic GCC model:
- Entity formation delays expose regulatory gaps and unclear compliance ownership
- Employment contract errors increase legal risk and reduce workforce trust
- Payroll inaccuracies trigger penalties, audits, and reputational exposure
- Data security gaps create cross-border compliance risks and trust issues
- Office, vendor, and facilities non-compliance disrupts operations
- Weak HR governance causes disputes, inconsistent policies, and cultural fragmentation
- Misaligned HQ–India ownership creates accountability gaps and escalation failures
- Poor IP protection and offboarding controls increase long-term security risks
- Overdependence on vendors reduces strategic control and flexibility
- Copying HQ structures limits speed, autonomy, and local decision-making
- Weak governance slows decisions and isolates GCCs from enterprise priorities
- Misaligned talent strategies drive attrition and capability gaps
- Treating GCCs as cost centers limits innovation and impact
- Lack of scalability planning forces costly operating model redesigns
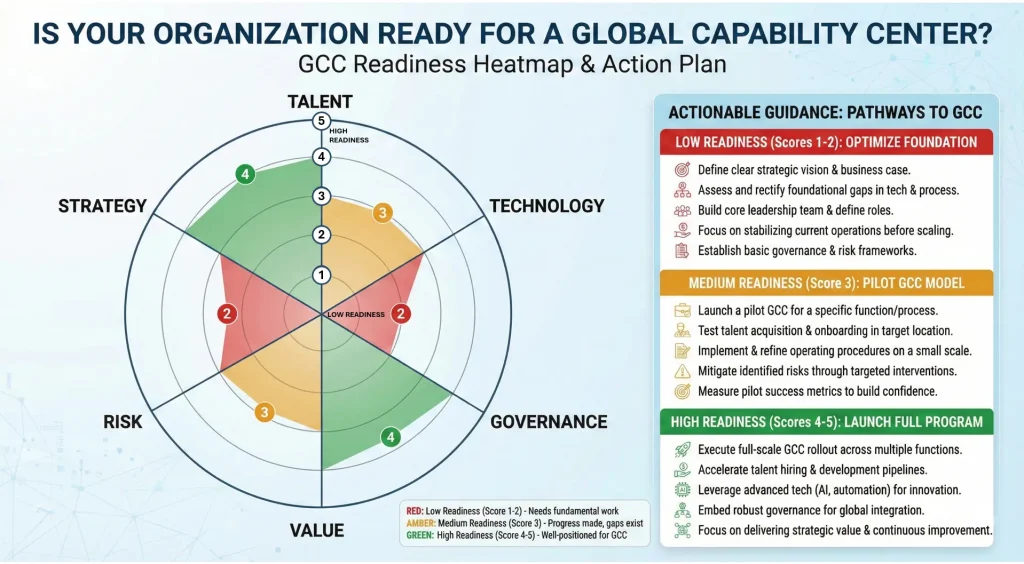
The GCC Readiness Assessment Framework
GCC readiness assessment begins by evaluating strategic clarity and leadership commitment. Without sponsorship, GCCs struggle to evolve beyond delivery-focused operating models. Leadership alignment determines whether GCCs become innovation hubs or remain cost centers.
Strategy and Leadership Sponsorship
This framework evaluates whether strategy and leadership can support GCC evolution beyond delivery. It focuses on alignment, sponsorship, and governance required for sustained enterprise impact. Here is a GCC readiness checklist you can follow for strategy and leadership:
- Strategic alignment is measured through HQ’s engagement with GCC initiatives and priorities
- Integration of GCC leadership into enterprise-wide decision-making and global operations
- Leadership effectiveness in driving change, adoption, and cultural transformation
- Innovation outcomes tracked through project acceleration, time-to-market, and R&D expansion
- Leadership impact is linked to innovation KPIs, not only cost or efficiency metrics
- Maturity assessment tracking progression- from cost efficiency to global integration stages
- Governance structures defining accountability, decision rights, and operational transparency
- Clear ownership of strategy execution across people, processes, and technology
Talent, Capability Depth, and Scalability
These offshore center health check factors assess whether talent depth and ecosystems can sustain long-term growth in the GCC. They focus on availability, capability maturity, and readiness to scale beyond initial phases. Together, these indicators determine whether a GCC can scale capabilities without losing stability:
- Assess access to diverse, skilled talent pools that support long-term GCC expansion
- Evaluate talent sophistication across digital, engineering, R&D, and emerging technologies
- Measure ecosystem strength, including startups, universities, and industry partnerships
- Review STEM graduate availability to sustain future capability pipelines
- Examine workforce employability and readiness for faster onboarding and productivity
- Assess leadership talent depth required to scale governance and strategic ownership
- Evaluate internal upskilling frameworks and continuous learning maturity
- Review the adoption of skills-first hiring to access niche and future-ready capabilities
- Assess government skilling and policy support enabling workforce scalability
- Evaluate infrastructure readiness for rapid expansion without productivity trade-offs
- Assess geographic talent distribution to reduce concentration and attrition risks
- Test scalability planning against five-to-ten-year capability and growth projections
Process, Technology, and Governance Maturity
This GCC readiness checklist assesses whether GCCs can scale securely, compliantly, and efficiently. It evaluates process discipline, technology foundations, and governance readiness for integration.
- Evaluate process maturity across consolidation, optimization, standardization, and transformation stages
- Benchmark workflows against peers to identify efficiency gaps and performance improvement opportunities
- Assess automation, cloud adoption, and platform engineering maturity, enabling faster innovation cycles
- Review DevOps pipelines supporting secure, scalable, and compliant technology delivery
- Evaluate data governance practices, ensuring hygiene, transparency, and enterprise-wide analytics readiness
- Assess AI governance, ethical usage standards, and model transparency requirements
- Review compliance readiness across data privacy, ESG reporting, and regulatory mandates
- Assess governance structures defining accountability, decision rights, and escalation mechanisms
- Evaluate reporting cadence, providing board-level visibility into risks and KPI trends
- Review the adoption of global frameworks such as ISO, COSO, COBIT, and zero-trust security
Diagnosing Your Existing Offshore or Nearshore Centers
Diagnosing existing offshore or nearshore centers requires evaluating performance, risk, and dependency indicators. It highlights delivery consistency, compliance exposure, and reliance on vendors or key individuals. These indicators determine whether current models can scale sustainably or require strategic restructuring.
Performance Indicators
- Quality of hires measured through retention rates, performance reviews, and manager feedback
- Time-to-fill trends highlight hiring efficiency and recruitment bottlenecks
- Cost per hire compared against local benchmarks to assess efficiency
- Effectiveness of sourcing channels based on candidate quality and conversion rates
- Candidate experience scores reflect employer brand strength and hiring process maturity
- Productivity tracked using task completion rates, velocity, and handling times
- Quality control indicators measure error rates and documentation accuracy
- Client feedback scores evaluate service quality and responsiveness
- Team response times tracked across task acknowledgment and completion
- Goal achievement rates aligned with SMART objectives
- Communication effectiveness measured through clarity and cultural alignment
- Employee engagement indices indicate long-term performance sustainability
Risk Indicators
- Lack of pricing transparency signals hidden costs and weak governance
- Vague SLAs or KPIs indicate accountability gaps and unclear expectations
- High employee turnover disrupts continuity and reduces delivery quality
- Unclear team structures create dependency on individuals over processes
- Outdated technology stacks increase security risks and inefficiencies
- Missing security certifications raise data protection and compliance risks
- Cultural or language mismatches reduce communication effectiveness and client experience
- Absence of disaster recovery plans threatens service continuity
- Overpromised outcomes without metrics indicate unreliable delivery
- Weak contracts expose intellectual property, data ownership, and exit risks
Dependency Indicators
- Heavy reliance on individual account managers increases operational and knowledge risks
- High turnover causes repeated retraining and dependency on external providers
- Limited internal visibility into workflows signals overdependence on vendors
- Weak KPI ownership reduces control over quality, timelines, and delivery
- Dependence on vendor-selected tools limits flexibility and decision-making autonomy
- Inadequate security oversight increases reliance on partner compliance assurances
- Language or cultural gaps heighten dependence on intermediaries
- Absence of documented processes increases reliance on tribal knowledge
- Scaling requires vendor intervention, indicating insufficient internal capability
Identifying Gaps That a GCC Can Close
- Limited ownership and control over teams restricts innovation and strategic alignment
- Task-focused delivery models prevent solving complex, high-impact business problems
- Overreliance on outsourcing reduces product ownership, loyalty, and institutional knowledge
- Fragmented provider models increase coordination complexity, costs, and delivery risks
- Short-term cost focus overshadows productivity, quality, and long-term innovation
- Inconsistent technology maturity slows digital transformation and capability development
- Weak integration with headquarters limits enterprise-wide influence and decision-making
- Location decisions driven by cost ignore talent depth, scalability, and ecosystem strength
- Managed delivery models limit evolution into centers of excellence and innovation hubs
- Lack of hybrid operating flexibility restricts the balance between speed, control, and scalability
From Audit Insights to an Actionable GCC Roadmap: Best Practices
GCC audit framework findings create value only when translated into clear, prioritized GCC actions. A structured roadmap converts insights into scalable, strategic execution. Here is the GCC readiness checklist you can follow:
- Align GCCs with Enterprise Strategy Beyond Cost Arbitrage: Reposition GCCs from transactional cost centers to value-driven strategic partners. Anchor GCC mandates enterprise priorities across innovation, data, and digital transformation.
- Use Digital Transformation as the Primary Scaling Lever: Assess digital maturity across automation, cloud adoption, cybersecurity, and core platforms. Prioritize end-to-end process automation to unlock speed, agility, and scalability.
- Build a Resilient Talent and Skills Engine: Shift from short-term hiring to continuous upskilling and future-ready capability building. Leverage universities, EdTech platforms, and remote-first models for sustained talent access.
- Embed Security and Compliance by Design: Adopt zero-trust architectures and global data privacy compliance frameworks early. Use AI-driven threat intelligence to proactively detect and mitigate security risks.
- Plan for Geopolitical Risk and Business Continuity: Diversify GCC locations to reduce concentration and geopolitical exposure. Use scenario planning and predictive analytics to strengthen operational resilience.
- Integrate ESG into GCC Operating Models: Embed sustainability, ethical governance, and carbon accountability into GCC performance metrics. Leverage AI to track ESG KPIs, energy usage, and compliance transparently at scale.
GCC readiness depends on conducting an honest audit of existing offshore or nearshore operations. An ideal GCC readiness assessment evaluates performance consistency, risk exposure, leadership alignment, and vendor dependencies. Organizations acting on these insights can move from costly delivery to strategic capability ownership.
ANSR supports this journey through readiness audits, operating model design, and phased transitions to building GCC in India. Contact us today to understand your GCC readiness and implement the transition effectively.




