How to Register and Set Up a Legal Entity: All You Need to Know
Expanding operations into India requires one to register a legal entity in India. This necessitates various strategic decisions, starting with the choice of a legal entity that best fits business goals. Navigating the regulations and compliance requirements is the first step to doing this successfully.
In this piece, we will share a comprehensive overview of the various aspects of setting up a legal entity in India, covering structures such as Private Limited Companies and LLPs, the step-by-step registration process, and the essentials of ongoing entity management to ensure compliance.
What is a Legal Entity and Why is it Essential for Setting up a GCC in India?
Establishing a legal entity is the first and most critical step in setting up a Global Capability Center (GCC) in India. A legal entity provides your business with a distinct corporate identity, separate from the personal liabilities of its promoters or parent organization. This legal separation ensures that the entity can operate independently, comply with local regulations, and assume full responsibility toward its stakeholders.
By forming a legal entity in India, a GCC gains the ability to:
- Own and manage assets, including office space, technology infrastructure, and equipment.
- Enter into legally binding contracts with employees, vendors, and clients.
- Open and operate local bank accounts for seamless financial transactions.
- Manage taxation and regulatory filings in compliance with Indian law.
- Represent itself in legal or commercial proceedings when required.
Governed by frameworks such as the Companies Act, 2013, a registered entity not only ensures compliance but also enhances credibility with regulators, employees, and partners. For global enterprises, this step establishes the foundation for sustainable operations and long-term success in one of the world’s most dynamic talent markets.
Why Forming a Legal Entity Matters for Your GCC in India
- Builds Trust and Credibility
A registered entity instills confidence among regulators, banks, clients, and potential partners. It signals professionalism and commitment, both of which are critical when establishing a GCC in a new market.
- Enables Strategic Growth
Whether entering partnerships, hiring talent at scale, or attracting investment, a formal legal structure is indispensable. It creates the governance framework required to expand operations responsibly and sustainably.
- Ensures Continuity and Stability
A registered company has a life beyond its founders or initial promoters. This permanence provides assurance to stakeholders that the GCC will operate with consistency, even through leadership transitions or ownership changes.
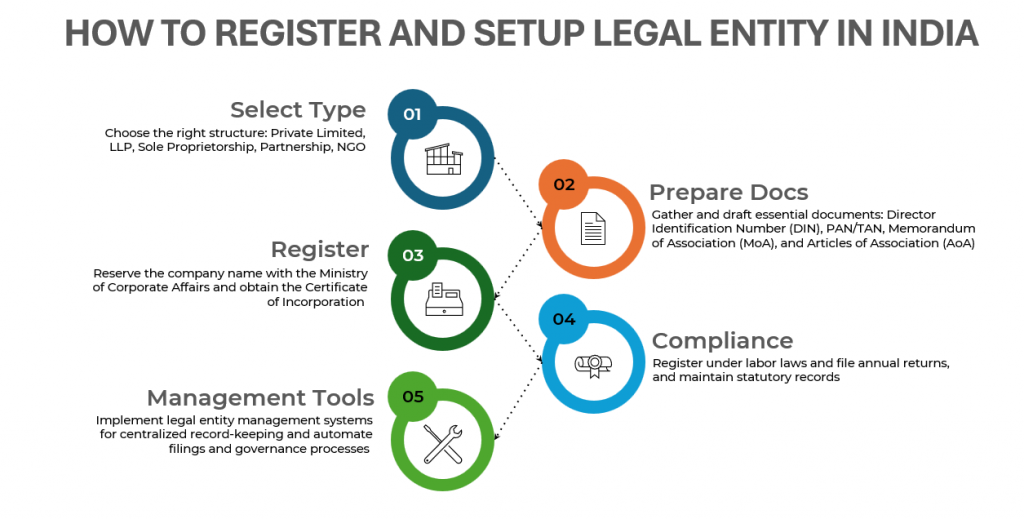
Choosing the Right Type of Legal Entity in India
Starting a business in India means deciding on the right legal structure, which affects taxes, liability, and how the business operates. There are several common types of legal entities in India to consider.
Sole Proprietorship
The simplest structure, owned and managed by a single individual. While easy to establish, the lack of separation between the owner and the business means full personal liability, making it unsuitable for large-scale or strategic operations like a GCC.
Partnership
It involves two or more people working together. In a general partnership, all partners share responsibility and liability equally. Limited partnerships have general partners with full liability, while limited partners only risk what they invest. Partners benefit from shared decision-making, and profits are taxed only once at the individual level.
Corporations
They are separate legal entities from their owners, protecting them from personal liability. There are C-Corporations, which face corporate tax but allow unlimited shareholders. On the other hand, S-Corporations avoid double taxation but limit the number of shareholders.
Limited Liability Companies (LLCs)
They combine features of partnerships and corporations. LLCs protect owners from personal risk and offer flexible tax options.
Non-profit Organizations
They exist to serve social and educational causes. They usually enjoy tax benefits and receive donations to support their cause.
Registration Process and Compliance Steps
To register a legal entity in India, one needs to follow a clear path. First, they need to choose a business structure and get a Digital Signature Certificate (DSC). After this, directors need to apply for a Director ID Number (DIN) and reserve a unique company name. Preparing the key founding documents, the Memorandum of Association (MoA) and Article of Association (AoA) and filing them with the Registrar of Companies.
After completing the entire process, an organization can get a Certificate of Incorporation in India. A company also needs to apply for a Permanent Account Number (PAN) and a Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number (TAN). Following all relevant labor laws is also crucial and so is filing the company’s annual returns on time. Staying compliant helps companies avoid any future penalties and ensures that a business can operate smoothly.
Legal Entity Management Systems for Indian Businesses
This refers to a governance system that includes different facets relating to organizational management. Legal management systems control and compile corporate records, including directors’ accounts, ownership structures, tax strategies, and more. They can also cover multiple departments of an organization, such as legal, tax, compliance, and human resources (HR). Check out the key benefits of these systems:
- Centralized Data Management
It brings all important entity information together in one secure place, which makes it easier for legal teams to access and update details and monitor compliance deadlines.
- Automation of Repetitive Tasks
These solutions can handle routine activities such as filing annual returns, updating director details, and generating compliance reports automatically. This cuts down on manual errors and frees up legal professionals to concentrate on more strategic work.
- Real-Time Reporting and Insights
Its dashboards and reporting features give immediate insight into compliance status, governance performance, and potential risks.
- Simplified Regulatory Compliance
With features like built-in compliance checklists, this software helps organizations stay compliant even in complicated regulatory landscapes.




